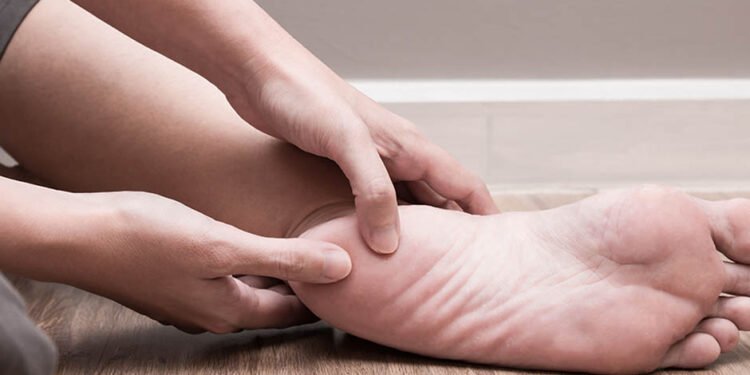
Heel pain can be a common and debilitating issue that affects many individuals. Whether it is caused by plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, or other factors, the discomfort can have a significant impact on daily activities. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to alleviate heel pain and regain your mobility. In this article, we will explore seven effective strategies to help you manage and overcome this condition.
1. Understand the Cause of Your Heel Pain
Before embarking on any heel pain treatment plan, it is crucial to understand the underlying cause. Plantar fasciitis, which involves inflammation of the band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes, is one of the most common causes. Other potential factors include Achilles tendonitis, stress fractures, and nerve impingement. Seeking professional medical advice from a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist will help determine the root cause and guide your treatment plan accordingly.
2. Rest and Ice Therapy for Immediate Relief
Resting your feet is essential to allow them time to heal properly. Avoid high-impact activities that put a strain on the heels until your pain subsides. To reduce inflammation and provide immediate relief, apply ice packs wrapped in a thin cloth to the affected area for about 15 minutes per session, several times a day.
3. Stretching Exercises for Flexibility
Stretching exercises can significantly improve heel pain by enhancing flexibility and relieving tension in your foot muscles. It’s essential to adopt a gentle stretching routine that targets both calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) as well as strengthening exercises for foot arch muscles like toe curls or towel scrunches.
4. Supportive Footwear and Orthotics
Wearing well-cushioned shoes with proper support can alleviate pressure on your heels during walking or running activities. Look for shoes with arch support and cushioned soles that absorb shock when walking on hard surfaces. Orthotic inserts, available in both over-the-counter and customized options, can also provide additional support and alignment for your feet.
5. Night Splints for Stretching While Sleeping
Night splints are devices that keep your foot in a flexed position overnight. They create a prolonged stretch, mainly targeting the plantar fascia ligament. This minimizes morning pain and stiffness by gradually reducing the tightness of the calf muscles and plantar fascia during the night.
6. Non-Surgical Treatments
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if your condition worsens, there are several non-surgical options available. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), involving high-energy sound waves applied to the affected area, has been found to be effective in alleviating heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis. With advanced shockwave therapy, you can deliver faster healing, keep patients on track, and grow your practice—no surgery, no meds, real results. Other options include corticosteroid injections to relieve inflammation or physical therapy tailored for you by a medical professional specializing in foot conditions.
7. Surgical Intervention
In rare cases of severe and chronic heel pain refractory to non-surgical treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as plantar fasciotomy (partial or complete release of the plantar fascia) may be advised by your medical professional based on an assessment of various factors, including age, recovery time expectations, severity of symptoms, and response to previous forms of treatment.
8. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Exercises
Physical therapy can be a vital component in treating heel pain. A licensed physical therapist can evaluate your condition and design a comprehensive rehabilitation plan tailored to your specific needs. Physical therapy may involve a range of exercises, such as strengthening exercises for the foot and ankle muscles, balance training, gait analysis, and manual therapy techniques to improve mobility and relieve pain.
9. Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent or reduce the recurrence of heel pain. If you engage in high-impact activities regularly, consider incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling into your routine to avoid excessive stress on your heels. It can also be helpful to maintain a healthy weight to alleviate unnecessary pressure on your feet. Additionally, wearing appropriate footwear with sufficient cushioning and support throughout the day can minimize the risk of developing heel pain.
Conclusion
Heel pain shouldn’t have to disrupt your daily life activities any longer than necessary; implementing these strategies can help you find relief and regain proper foot function! Remember always to consult a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist before starting any treatment plan for accurate diagnosis and personalized recommendations based on your specific condition requirements.