Article by Hearing Partners, contributed by Joey Fong, Clinical Audiologist at Hearing Partners
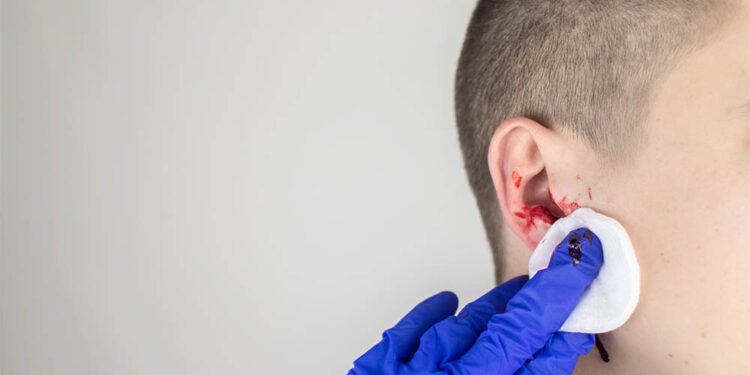
If you notice any blood inside or coming out of your ear, your ear could be bleeding. This could occur due to various reasons and while it typically does not cause complications, the underlying causes can potentially lead to long-term issues.
This article will explore the reasons behind your ear bleeding, when it is advisable to seek medical attention and the commonly recommended treatment options. Read more below!
Note: If you experienced a head injury recently and notice blood from your ears, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention by either calling an ambulance or heading to the emergency room. Ear bleeding following a head trauma could be a sign of a life-threatening situation that requires prompt medical intervention.
Causes of Bleeding Ears
A variety of factors can cause your ear to bleed including:
Skin injury

Scratching your ear canal with your fingernail or inserting a cotton swab too deeply can result in bleeding. Most often, such injuries are not severe. It is crucial to keep the wound clean to prevent any potential infections.
Ear infection
Ear infections in the middle ear and outer ear can cause discharge and blood, and may lead to a ruptured eardrum. It usually accompanies the following symptoms: pain or pressure in the ear, swelling, and hearing changes.
Ruptured eardrum
The eardrum is a thin membrane between the outer and middle ear. When this membrane tears or ruptures due to rapid changes in atmospheric or water pressure (such as those experienced during air travel or scuba diving), loud noise exposure, ear infections, or physical trauma, bleeding may occur.
Foreign objects in the ear
When you stick objects into your ears, the object can become dislodged or stuck in the ear canal, causing abrasions on the skin or tears in the eardrum. This can subsequently lead to pain and bleeding in the ear.
Trauma and head injury
A head injury or accident can lead to ear bleeding, which can be a sign of internal bleeding and skull fracture. In such cases, immediate medical assistance is crucial as it could be life-threatening.
Ear cancer
Ear cancer is rare and can develop in any part of the ear. It usually starts in the skin of the outer ear and can spread further into the middle and inner ear. When ear cancer is the cause, the following symptoms may accompany ear bleeding or bloody discharge:
- Hearing loss
- Ear pain/fullness
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Facial weakness
When to See a Doctor
If your ear is bleeding, it is recommended to consult an Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) doctor for a thorough examination. This is especially important when the bleeding is accompanied by symptoms such as pain, swelling, discharge or fever.
Identifying the underlying cause of the bleeding or infection is essential to ensuring appropriate treatment. For example, if an object is lodged in your ear canal and isn’t easily visible, a medical professional can help to safely remove it from your ear, preventing any cuts or abrasions in the process.
However, if your ears are bleeding following an accident or a blow to the head, it could indicate a potentially life-threatening injury. Immediate medical attention is required if you experience the following symptoms in addition to ear bleeding:
- Nosebleed
- Dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Vision issues
- Hearing loss
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
How to Treat Bleeding Ears
The ENT doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination, gather information about your medical history, and inquire about the onset of the bleeding and any possible contributing factors.
The doctor may also request a hearing test or an imaging or laboratory test to confirm the diagnosis or identify further complications. Subsequently, a suitable treatment plan will be prescribed based on the underlying cause of the bleeding.
Antibiotics

If an ear infection is the cause of the bleeding, your doctor might prescribe oral antibiotics or antibiotic ear drops.
Ear tubes
In the event of an ear infection, the doctor might relieve pressure and remove fluid from your ear by inserting tubes into your eardrums.
Removal of foreign objects from the ear
Should a foreign object become lodged in your ear, the doctor will extract it using the appropriate tools to prevent any harm to your ear canal.
Tympanoplasty
In most instances, a ruptured eardrum can heal naturally. However, if it fails to do so, tympanoplasty may be necessary. Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure where any tears or damage to your eardrum is repaired.
FAQs About Ear Bleeding
What causes bloody drainage from the ear?
Ear infection and ruptured eardrum can result in discharge or drainage that’s white, slightly bloody or yellow. If you’re unsure, we recommend checking with an ENT doctor.
Will there be complications if my ear bleeds?
Bleeding from your ears typically won’t lead to complications, but the underlying causes can lead to long-term issues. Common complications of ear bleeding causes include:
- Changes to language perception
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- Cognitive difficulties
- Headaches
- Vertigo
- Balance problems